Frequently Asked Questions
Wastewater Lift Stations
How do I set the Float Control?
- Typical Float Switch Setting (PDF).
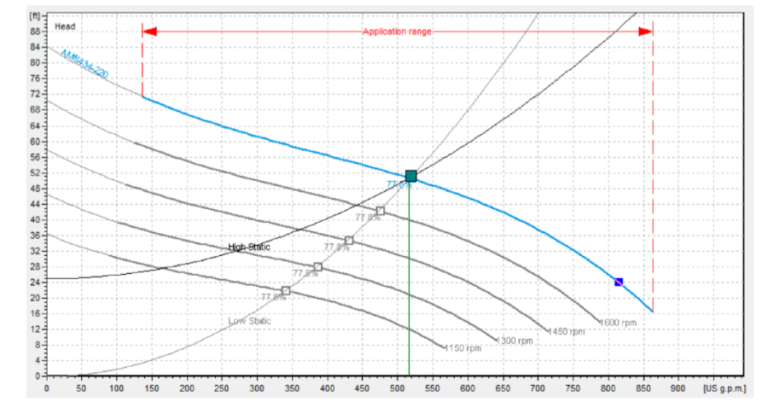
What is “Head Pressure”?
- Head is typically expressed in units of height, such as meters or feet. The static head of a pump refers to the maximum height (or pressure) it can deliver. In most cases, you can read the pump’s capability at a specific RPM from its Q-H curve (flow vs. height). Head represents the fluid’s energy per unit of weight. Additionally, factors such as the length and diameter of the force main, elevation change, and flow rate in gallons per minute all play a role in determining head pressure.
What diameter of force main do I need?
- Force mains are typically sized to achieve a flow velocity between 3 and 5 feet per second, which helps prevent solids from settling. Therefore, it’s important to evaluate flow requirements and line distance when choosing a diameter.
What is a “Grinder Pump” and what are the benefits of a “Grinder Pump”?
- A grinder pump uses a grinding mechanism—similar to a garbage disposal—to shred solid waste into a slurry. As a result, the pump does not need to move any solids. This allows for the use of a smaller diameter force main, which can be more cost-effective in many applications.
What is the difference between a “Non-Clog” sewage pump and a “Grinder Pump”?
- A Non-Clog pump is designed to pass solids of a certain size without clogging. By contrast, a grinder pump breaks the solids down into a slurry, eliminating the need to pump solid materials. Therefore, each type serves a different purpose depending on the system design and waste content.
What is an “Influent Line” and why do you need to know its depth?
- Simply put, the influent line is the sewer pipe that brings wastewater into the lift station from a house or building. Knowing the depth of the influent line is important for several reasons. First, it must be below the frost line to prevent freezing. In addition, the area below the influent line determines how much room is available for sewage storage and pump operation. Therefore, the basin depth is partially determined by how deep the influent line is buried.
What size of a basin do I need?
- The correct basin size depends on several factors, including the amount of sewage to store and pump, the depth of the influent line, and the number of people being served. For this reason, each of these elements must be evaluated together to determine an appropriate basin volume.
How do I know how many “Gallons Per Minute” I need to pump?
- Gallons per minute (GPM) is usually calculated based on the number of people the lift station will serve. To size the system properly, it’s important to consider peak flow, total population, and sometimes even the number of plumbing fixtures involved.
What does an FRP basin mean?
- FRP stands for Fiberglass Reinforced Poly. This material offers strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion, making it a reliable choice for lift station basins.
What is the difference between a “Simplex Lift Station” and a “Duplex Lift Station”?
- A simplex lift station contains one pump and the controls for that pump. A duplex lift station, on the other hand, includes two pumps and controls that allow them to alternate. In some larger applications—such as municipal systems—stations may even include three (triplex) or more pumps.
What are the benefits of having a “Duplex Lift Station” over a “Simplex Lift Station”?
- With a duplex lift station, the biggest benefit is redundancy. If one pump fails, the second pump automatically provides backup. In addition, the system alternates between pumps, helping to ensure even wear and reduce the chance of mechanical failure from overuse.
How long should a pump last before it needs to be replaced?
- The lifespan of a pump varies depending on usage and maintenance. Generally speaking, a well-maintained pump will last for many years. However, heavy usage or poor maintenance can significantly shorten its life expectancy.
What electrical service is required for the pumps in a lift station?
- Most residential sewage and grinder lift stations require 230-volt, single-phase power. In contrast, larger systems for municipalities or industrial applications often need 460-volt, three-phase service. Fortunately, manufacturers can build pumps in various combinations of phase and voltage to suit different requirements.